New evidence highlights further concern about chlorhexidine allergies in healthcare

A new hospital study1 has revealed a high reported use of chlorhexidine and the presence of skin problems in more than a quarter of health care workers.
Key findings showed:
- More than 95% of the 1000 people questioned used chlorhexidine-based hand hygiene products in their workplace.
- 7% of nurses and midwives reported asthma symptoms
- 8% of nurses and midwives complained of contact dermatitis
The new findings come only a few months after the NAP6 report 2 which revealed that 9% of anaphylaxis cases in surgical patients had been triggered by an allergic reaction to chlorhexidine.
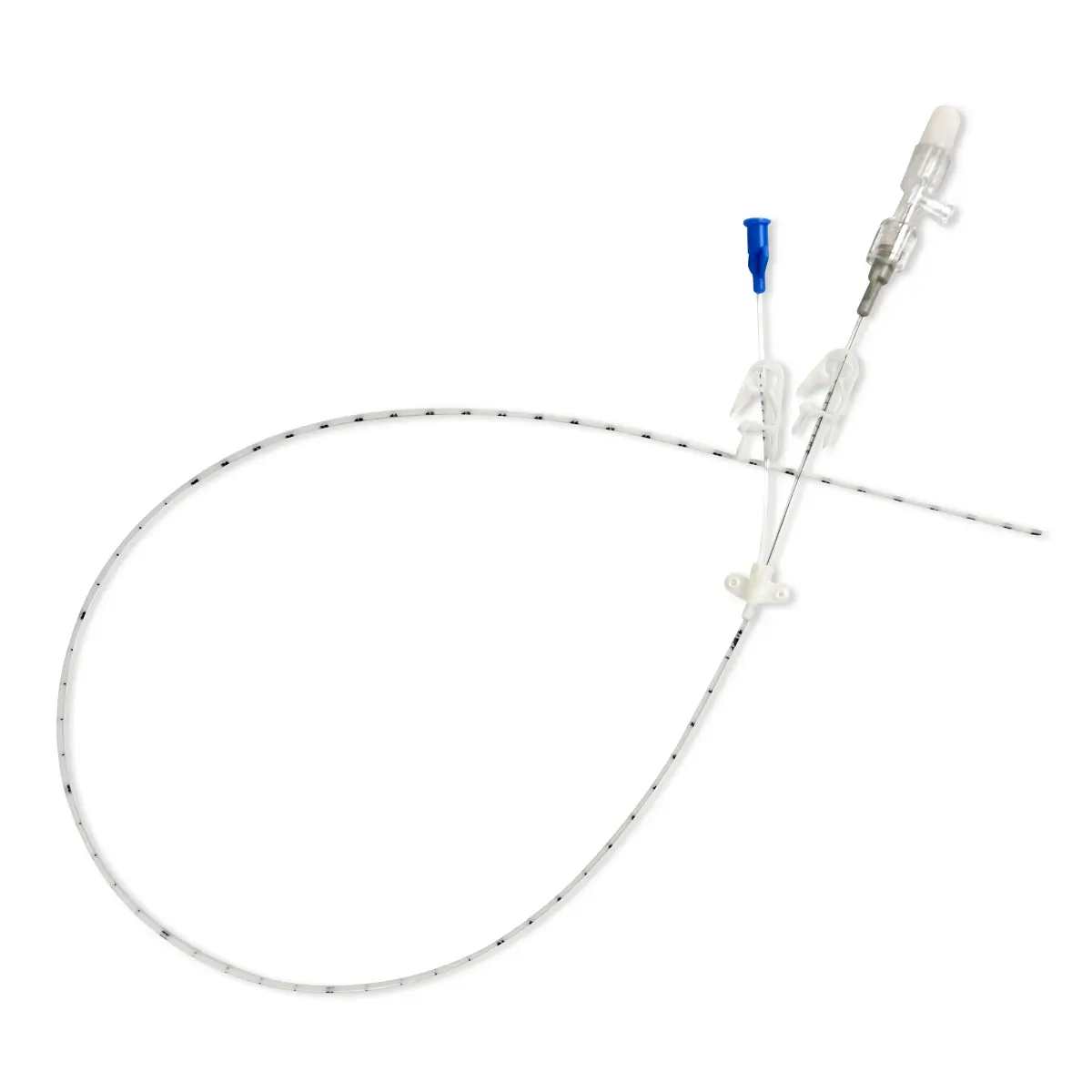
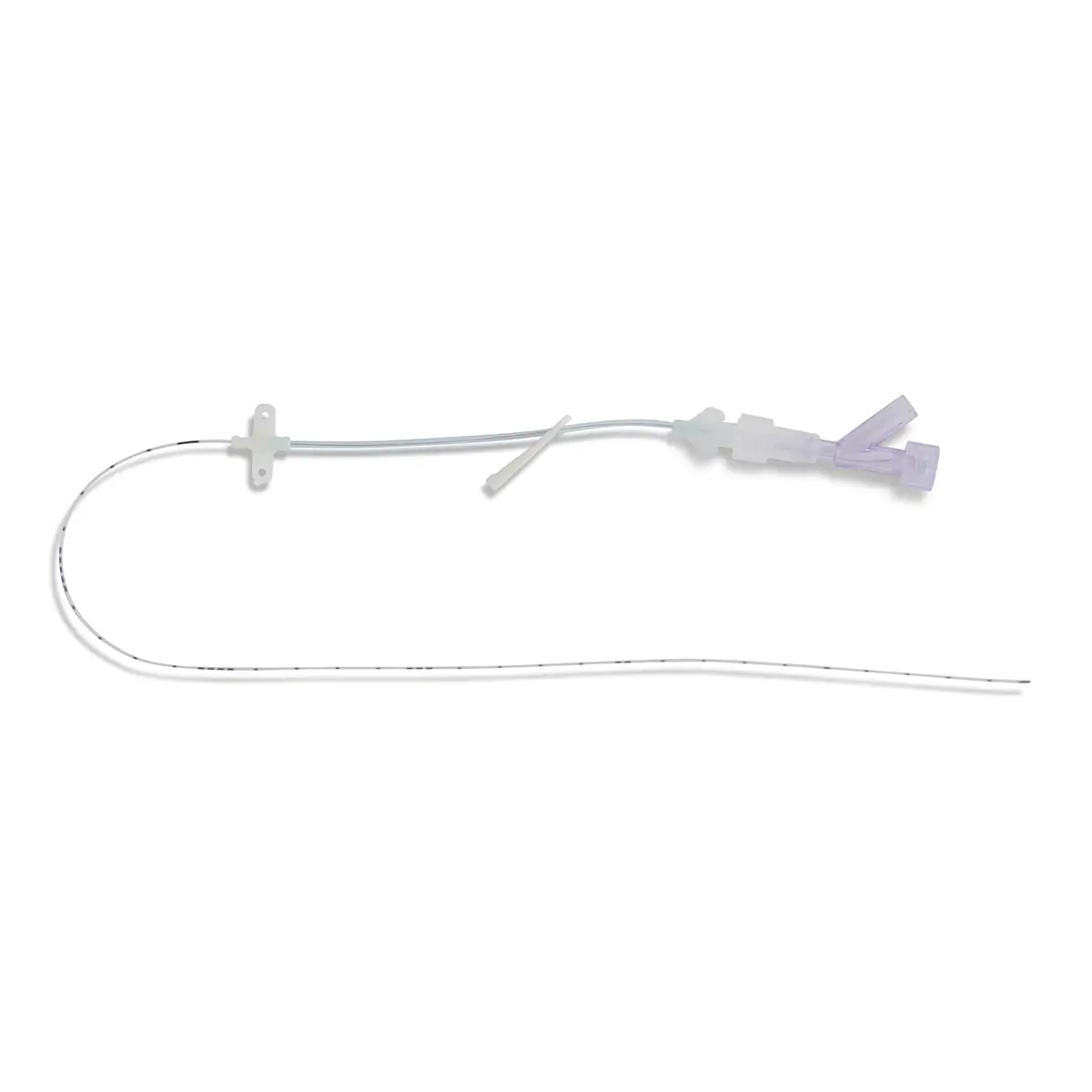
As it isn’t immediately obvious that some medical devices and equipment, such as anti microbial central venous catheters, contain chlorhexidine, it has been described as the ‘hidden allergen’3.
For more information about NAP 6 and the steps to take to avoid unnecessary exposure to chlorhexidine
References:
1 Barnes, S. et al. Health care worker sensitivity to chlorhexidine-based hand hygiene solutions: A cross-sectional survey American Journal of Infection Control 2019
2 The 6th National Audit Project of the Royal College of Anaesthetists (NAP6) Survey results: Anaesthesia, Surgery, and Life-Threatening Allergic Reactions
3 Ebo 2004: Ebo DG, Bridts CH, Stevens WJ. Anaphylaxis to an urethral lubricant: Chlorhexidine as the “hidden” allergen. Acta Clinica Belgica 2004; 59: 358–60.
Published 8th March 2019